- Services
- Case Studies
- Technologies
- NextJs development
- Flutter development
- NodeJs development
- ReactJs development
- About
- Contact
- Tools
- Blogs
- FAQ
Understanding CSS fill-opacity for SVG Graphics
Learn how to use it with numeric and percentage values to create visually appealing designs.
Introduction
The fill-opacity property in CSS is used to control the opacity of the fill color applied to SVG shapes and text content elements. This property ensures consistent rendering across different browsers and devices, making your SVG graphics look great everywhere.
By adjusting the fill-opacity, you can create amazing designs with varying levels of transparency. Whether you want a subtle, semi-transparent effect or a fully opaque fill, fill-opacity has got you covered.
Specification
The fill-opacity property is defined in the CSS Fill and Stroke Module Level 3 specification. This module outlines how fill and stroke properties should work for SVG elements, ensuring consistent rendering across different web browsers.
This property has been around for a while and is well-supported, so you can use it confidently in your web projects. The specification provides detailed guidelines, making sure your designs look consistent and appealing across various platforms and browsers.
Description
The fill-opacity property in CSS is used to define the transparency level of the fill color applied to SVG shapes and text content elements. It lets you control the opacity of the fill independently of the stroke, giving you the flexibility to create complex and visually appealing designs.
The fill-opacity property can take numeric values between 0 and 1 or percentage values between 0% and 100%. A value of 0 or 0% makes the fill color completely transparent, while a value of 1 or 100% makes it fully opaque. Values in between create a semi-transparent effect, allowing the background or underlying elements to show through.
This property is great for adding depth and dimension to your SVG graphics. By adjusting the fill-opacity, you can create layered effects, subtle gradients, and other visual techniques that enhance the overall aesthetic of your web designs.
Syntax
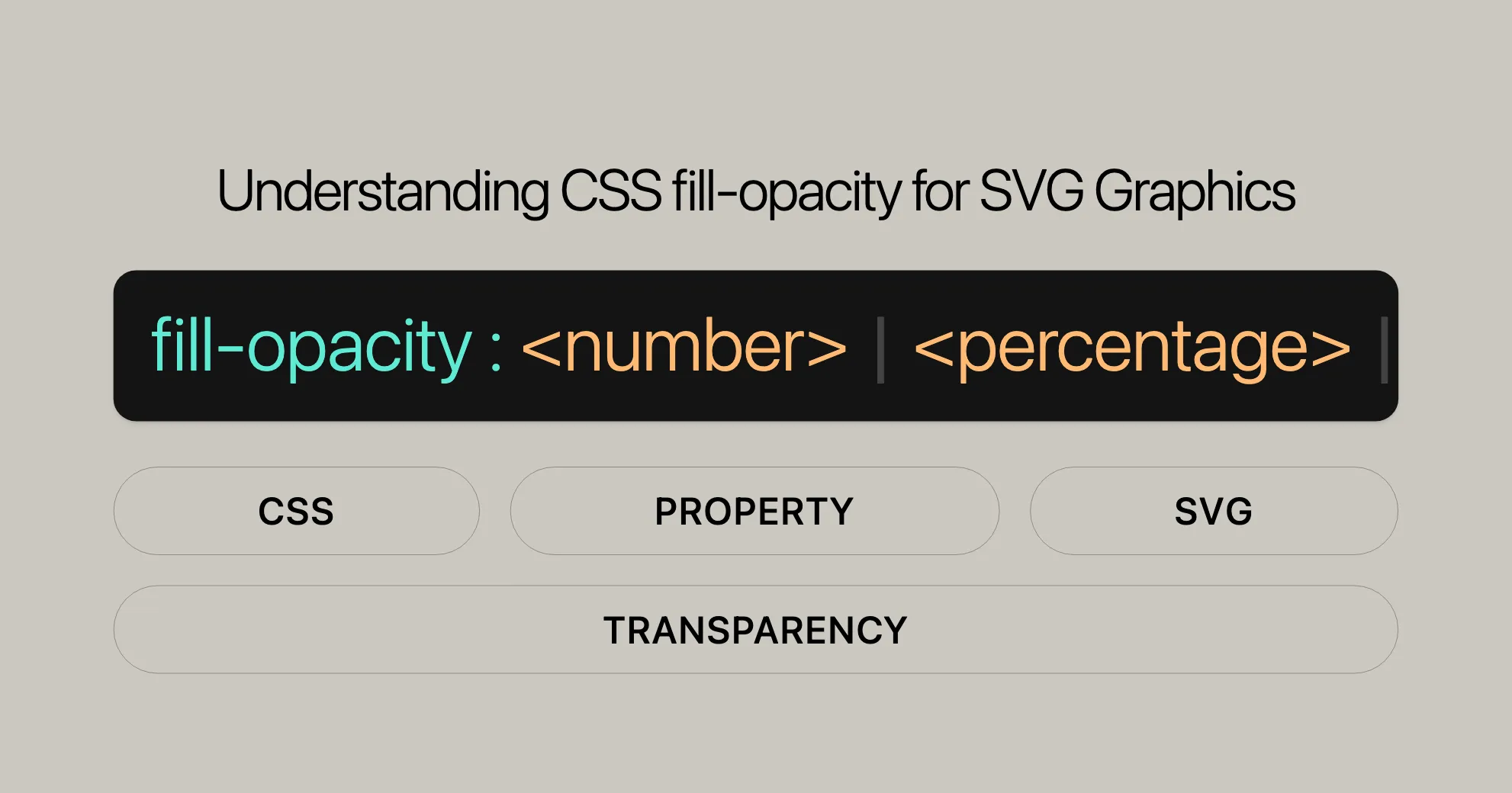
The fill-opacity property in CSS is easy to use. You can apply it to SVG shapes and text content elements to control the opacity of their fill color. Here’s the syntax:
fill-opacity: <number> | <percentage> | inherit | initial | revert | revert-layer | unset;Here’s a breakdown of the possible values:
<number>: A numeric value between0and1, where0is fully transparent and1is fully opaque.<percentage>: A percentage value between0%and100%, with0%being fully transparent and100%being fully opaque.inherit: The element inherits thefill-opacityvalue from its parent element.initial: The element uses the initial value of the property, which is1.revert: The element reverts to the value specified by the user stylesheet, if any.revert-layer: The element reverts to the value specified by the user stylesheet, if any, but only for the specified layer.unset: The element uses the default value of the property.
Using these values, you can easily adjust the transparency of the fill color to achieve the desired visual effect in your SVG graphics.
Values
The fill-opacity property can take two types of values: numeric values and percentage values.
Numeric Values
<number>: This value ranges from0to1. A value of0makes the fill color completely transparent, while1makes it fully opaque. Values in between create a semi-transparent effect.
Percentage Values
<percentage>: This value ranges from0%to100%. A value of0%makes the fill color completely transparent, while100%makes it fully opaque. Values in between create a semi-transparent effect.
Both numeric and percentage values provide the same level of control over the opacity of the fill color, allowing you to fine-tune the appearance of your SVG elements to suit your design needs.
Formal Definition
The fill-opacity property in CSS is formally defined to control the opacity of the fill color applied to SVG shapes and text content elements. This property is designed to manipulate the transparency of the fill, independent of the stroke. Here are the key aspects of its formal definition:
- Initial Value: The default value for
fill-opacityis1, which means the fill color is fully opaque. - Applies To: This property applies to SVG shapes and text content elements, such as
<circle>,<ellipse>,<path>,<polygon>,<polyline>,<rect>,<text>,<textPath>, and<tspan>. - Inherited: Yes, the
fill-opacityproperty can be inherited from parent elements. - Percentages: Percentage values map to the range
[0,1], where0%is fully transparent and100%is fully opaque. - Computed Value: The computed value is the same as the specified value after clipping the
<number>to the range[0.0, 1.0]. - Animation Type: The animation type is by computed value type.
This formal definition ensures that the fill-opacity property behaves consistently across different browsers and devices, providing web developers with a reliable tool for controlling the transparency of fill colors in their SVG graphics.
Formal Syntax
The fill-opacity property follows a specific syntax defined in the CSS specification. This syntax outlines the valid values and structure for applying the fill-opacity property to SVG elements. The formal syntax for fill-opacity is as follows:
fill-opacity = <opacity>
<opacity> = <opacity-value>
<opacity-value> = <number> | <percentage>Breakdown of the Syntax
<opacity>: This represents the opacity value that can be applied to the fill color of an SVG element.<opacity-value>: This can be either a numeric value (<number>) or a percentage value (<percentage>).
Detailed Explanation
<number>: A numeric value between0and1.0: The fill color is fully transparent.1: The fill color is fully opaque.- Values between
0and1: The fill color is semi-transparent.
<percentage>: A percentage value between0%and100%.0%: The fill color is fully transparent.100%: The fill color is fully opaque.- Values between
0%and100%: The fill color is semi-transparent.
This formal syntax ensures that the fill-opacity property can be applied correctly and consistently across different web browsers and devices, providing web developers with a reliable tool for controlling the transparency of fill colors in their SVG graphics.
Examples
Defining the Fill Opacity of SVG Elements
This example demonstrates the basic use case of fill-opacity, and how the CSS fill-opacity property takes precedence over the fill-opacity attribute and has no effect on any stroke applied to a shape.
HTML
In this example, we include several different SVG graphic elements and set the fill-opacity attribute of each one to 1. This means the fill of each element is opaque. The fill-opacity SVG attribute does not apply to <line>.
<svg viewbox="0 0 100 150" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"> <rect x="10" y="10" width="30" height="30" fill-opacity="1" /> <rect x="60" y="10" rx="10" ry="10" width="30" height="30" fill-opacity="1" /> <circle cx="25" cy="75" r="20" fill-opacity="1" /> <ellipse cx="75" cy="75" rx="20" ry="10" fill-opacity="1" /> <line x1="50" x2="90" y1="40" y2="60" stroke="black" stroke-width="5" /> <polyline points="60 90 65 100 70 95 75 110 80 105 85 120 90 115 95 130 100 125" fill-opacity="1" /> <path d="M20,130 Q40,105 50,130 T90,130" fill-opacity="1" /></svg>CSS
With CSS, we use the fill-opacity property to override the value of the SVG fill-opacity attribute, giving each SVG element a different value.
We also add a stroke to the circle and ellipse to demonstrate that the opacity of the stroke is not impacted by the fill-opacity property.
Other SVG styles are set, including a background image to allow the opacity of each element to be more easily seen. These are not shown for the sake of brevity.
svg { border: 1px solid; height: calc(100vh - 20px); background: repeating-linear-gradient( to bottom right, transparent 0 10px, #ccc 10px 11px );}
svg > * { fill: black;}
rect:last-of-type { fill-opacity: 0.1;}
circle { fill-opacity: 0.6;}
ellipse { fill-opacity: 40%;}
line { fill-opacity: 10%;}
polyline { fill-opacity: 50%;}
path { fill-opacity: 0.5;}
circle,ellipse { stroke: black; stroke-width: 3px;}Results
Only two elements are fully opaque: the first rectangle and the line. The first rectangle is not matched by any of the selectors, therefore no CSS is applied and the fill is fully opaque. The line is matched, with fill-opacity: 10% set. However, the line has no fill paint operation — only the stroke is visible — therefore the declaration has no effect.
See Also
To further enhance your understanding and usage of the fill-opacity property, you may find the following related resources and properties helpful:
Related SVG Attributes and Properties
- SVG
fill-opacityAttribute: Learn more about the SVGfill-opacityattribute, which the CSSfill-opacityproperty can override. - Presentation Properties: Explore other CSS properties used for SVG presentation, such as
clip-rule,color-interpolation-filters,fill-rule,fill,marker-end,marker-mid,marker-start,shape-rendering,stop-color,stop-opacity,stroke,stroke-dasharray,stroke-dashoffset,stroke-linecap,stroke-linejoin,stroke-miterlimit,stroke-opacity,stroke-width,text-anchor, andvector-effect.
General CSS Properties
opacity: This CSS property is used to set the opacity level of an entire element, including its content, children, and background.background-color: This property sets the background color of an element.<color>: Learn about the<color>data type in CSS, which defines colors.<basic-shape>: Discover the<basic-shape>data type, which is used to define basic shapes in CSS.
Additional Resources
- MDN Web Docs: Visit the MDN Web Docs for detailed documentation and examples on the
fill-opacityproperty. - Can I Use: Check the Can I Use website to stay updated on browser compatibility for the
fill-opacityproperty.
Contributing to MDN
If you find the information on the fill-opacity property helpful or have suggestions for improvement, consider contributing to the MDN documentation. Your feedback and contributions can make a significant difference in improving the resources available to web developers worldwide.
- Learn How to Contribute: Visit the MDN Contribution Guidelines to learn how you can contribute.
- View Page on GitHub: Access the GitHub repository for the
fill-opacitydocumentation. - Report a Problem: If you encounter any issues or have feedback, you can report it through the MDN GitHub Issues.
By exploring these related resources and contributing to the documentation, you can deepen your knowledge of CSS and SVG properties, enhancing your web development skills and creating more visually appealing and functional web designs.
Supported Browsers
The fill-opacity property is widely supported across a range of modern web browsers, ensuring that your SVG graphics render consistently across different platforms and devices. Here is a list of browsers that support the fill-opacity property:
- Google Chrome: Full support.
- Mozilla Firefox: Full support.
- Apple Safari: Full support.
- Opera: Full support.
- Microsoft Edge: Full support.
- Internet Explorer: Supported starting from version 9.
Compatibility Details
The fill-opacity property has been available and well-established since July 2020, making it a reliable choice for web developers and designers. Its broad compatibility ensures that your SVG graphics will look as intended across various browsers and devices.
Checking Browser Compatibility
To verify the compatibility of the fill-opacity property in different browsers, you can refer to the following resources:
- MDN Web Docs Compatibility Table: Provides a detailed overview of browser support for the
fill-opacityproperty. - Can I Use - fill-opacity: Offers up-to-date information on browser compatibility for various web technologies, including the
fill-opacityproperty.
Ensuring Consistent Rendering
To ensure that your SVG graphics render consistently across all supported browsers, it is essential to test your designs on multiple platforms. This will help you identify any potential issues and make necessary adjustments to maintain a consistent user experience.
Reporting Issues
If you encounter any issues or inconsistencies with the fill-opacity property, you can report them to help improve the documentation and implementation. Useful links for reporting issues include:
- MDN Feedback Survey: Share your feedback to help improve the documentation.
- MDN GitHub Issues: Report issues or provide feedback to enhance the
fill-opacityproperty documentation.
By understanding and using the fill-opacity property effectively, you can create more dynamic and visually appealing SVG graphics for your web projects. This property provides the flexibility needed to control the transparency of fill colors, enhancing the overall aesthetic of your designs.
 สร้างเว็บไซต์ 1 เว็บ ต้องใช้งบเท่าไหร่? เจาะลึกทุกองค์ประกอบ website development cost อยากสร้างเว็บไซต์แต่ไม่มั่นใจในเรื่องของงบประมาณ อ่านสรุปเจาะลึกตั้งแต่ดีไซน์, ฟังก์ชัน และการดูแล พร้อมตัวอย่างงบจริงจาก Till it’s done ที่แผนชัด งบไม่บานปลายแน่นอน
สร้างเว็บไซต์ 1 เว็บ ต้องใช้งบเท่าไหร่? เจาะลึกทุกองค์ประกอบ website development cost อยากสร้างเว็บไซต์แต่ไม่มั่นใจในเรื่องของงบประมาณ อ่านสรุปเจาะลึกตั้งแต่ดีไซน์, ฟังก์ชัน และการดูแล พร้อมตัวอย่างงบจริงจาก Till it’s done ที่แผนชัด งบไม่บานปลายแน่นอน  Next.js สอน 14 ขั้นตอนเบื้องต้น: สร้างโปรเจกต์แรกใน 30 นาที เริ่มต้นกับ Next.js ใน 14 ขั้นตอนเพียงแค่ 30 นาที พร้อม SSR/SSG และ API Routes ด้วยตัวอย่างโค้ดง่าย ๆ อ่านต่อเพื่อสร้างโปรเจ็กต์แรกได้ทันทีที่นี่
Next.js สอน 14 ขั้นตอนเบื้องต้น: สร้างโปรเจกต์แรกใน 30 นาที เริ่มต้นกับ Next.js ใน 14 ขั้นตอนเพียงแค่ 30 นาที พร้อม SSR/SSG และ API Routes ด้วยตัวอย่างโค้ดง่าย ๆ อ่านต่อเพื่อสร้างโปรเจ็กต์แรกได้ทันทีที่นี่  วิธีสมัคร Apple Developer Account เพื่อนำแอปขึ้น App Store ทีละขั้นตอน อยากปล่อยแอปบน App Store ระดับโลก มาอ่านคู่มือสมัคร Apple Developer Account พร้อมเคล็ดลับ TestFlight และวิธีอัปโหลดที่ง่ายในบทความเดียวนี้ได้เลย
วิธีสมัคร Apple Developer Account เพื่อนำแอปขึ้น App Store ทีละขั้นตอน อยากปล่อยแอปบน App Store ระดับโลก มาอ่านคู่มือสมัคร Apple Developer Account พร้อมเคล็ดลับ TestFlight และวิธีอัปโหลดที่ง่ายในบทความเดียวนี้ได้เลย  TypeScript Interface คืออะไร? อธิบายพร้อมวิธีใช้และข้อแตกต่างจาก Type เรียนรู้วิธีใช้ TypeScript Interface เพื่อสร้างโครงสร้างข้อมูลที่ปลอดภัยและเข้าใจง่าย พร้อมเปรียบเทียบข้อดีข้อแตกต่างกับ Type ที่คุณต้องรู้ ถูกรวมเอาไว้ในบทความนี้แล้ว
TypeScript Interface คืออะไร? อธิบายพร้อมวิธีใช้และข้อแตกต่างจาก Type เรียนรู้วิธีใช้ TypeScript Interface เพื่อสร้างโครงสร้างข้อมูลที่ปลอดภัยและเข้าใจง่าย พร้อมเปรียบเทียบข้อดีข้อแตกต่างกับ Type ที่คุณต้องรู้ ถูกรวมเอาไว้ในบทความนี้แล้ว  Material-UI (MUI) คืออะไร อยากสร้าง UI สวยงามและเป็นมืออาชีพในเวลาอันรวดเร็วใช่ไหม มาทำความรู้จักกับ Material-UI (MUI) ที่ช่วยให้คุณพัฒนาแอปพลิเคชันบน React ได้ง่ายและดูดีในทุกอุปกรณ์
Material-UI (MUI) คืออะไร อยากสร้าง UI สวยงามและเป็นมืออาชีพในเวลาอันรวดเร็วใช่ไหม มาทำความรู้จักกับ Material-UI (MUI) ที่ช่วยให้คุณพัฒนาแอปพลิเคชันบน React ได้ง่ายและดูดีในทุกอุปกรณ์  เปรียบเทียบ 3 วิธีติดตั้ง install node js บน Ubuntu: NVM vs NodeSource vs Official Repo แบบไหนดีที่สุด? เรียนรู้วิธีติดตั้ง Node.js บน Ubuntu ด้วย NVM, NodeSource หรือ Official Repo เลือกวิธีที่เหมาะกับความต้องการของคุณ พร้อมเปรียบเทียบ เพื่อการพัฒนาที่มีประสิทธิภาพ!
เปรียบเทียบ 3 วิธีติดตั้ง install node js บน Ubuntu: NVM vs NodeSource vs Official Repo แบบไหนดีที่สุด? เรียนรู้วิธีติดตั้ง Node.js บน Ubuntu ด้วย NVM, NodeSource หรือ Official Repo เลือกวิธีที่เหมาะกับความต้องการของคุณ พร้อมเปรียบเทียบ เพื่อการพัฒนาที่มีประสิทธิภาพ! Talk with CEO
We'll be right here with you every step of the way.
We'll be here, prepared to commence this promising collaboration.
Whether you're curious about features, warranties, or shopping policies, we provide comprehensive answers to assist you.


