- Services
- Case Studies
- Technologies
- NextJs development
- Flutter development
- NodeJs development
- ReactJs development
- About
- Contact
- Tools
- Blogs
- FAQ
Mastering CSS Zoom Enhance Web Design Responsiveness
Explore available options like normal, reset, percentages, and numbers.
Introduction
The zoom CSS property is a powerful tool for controlling the magnification level of an element on a web page. Introduced in May 2024, this feature works best with the latest devices and browser versions, although it might not work on older devices or browsers. The zoom property lets you scale elements, which affects the page layout. By default, the element scales from the top and center. Unlike zoom, the transform: scale() function scales elements without affecting the page layout or moving other elements. If the scaled content is larger than its container, the overflow property determines how the extra content is handled.
This article will guide you through the zoom property, covering its syntax, values, formal definition, and practical examples. You’ll learn how to resize paragraphs, elements, and create a zoom control using this property. We’ll also discuss browser compatibility and provide links to further resources for deeper learning.
By the end of this article, you’ll understand how to effectively use the zoom property in your web development and design projects, enhancing the user experience with dynamic and responsive elements.
Specification
The zoom property is defined in the CSS Viewport Module Level 1 specification. This module outlines the behavior and usage of the zoom property, providing a standardized approach for web developers to implement zoom functionalities across different browsers and devices.
For detailed information and the latest updates on the zoom property, you can refer to the official specification:
- [CSS Viewport Module Level 1 - Zoom Property]WebsiteUrl
This specification is a valuable resource for understanding the technical aspects and implementation details of the zoom property, ensuring consistency and compatibility in web development projects.
Description
The zoom CSS property controls the magnification level of an element on a web page. This property scales the targeted element, which can directly impact the overall layout of the page. When zooming, the element scales from the top and center by default, unless otherwise specified.
The zoom property is particularly useful for adjusting the size of content dynamically, making it easier to create responsive designs that adapt to different screen sizes and user preferences. However, it’s important to note that the zoom property affects the layout of the page, which means other elements may be repositioned or resized as a result.
An alternative to the zoom property is the transform: scale() function. Unlike zoom, transform: scale() scales elements without causing layout recalculation or moving other elements on the page. If the scaled content exceeds the boundaries of its container, the overflow property will determine how the overflowing content is handled. Additionally, transform: scale() scales elements from the center by default, but this behavior can be modified using the transform-origin property.
Understanding the differences between zoom and transform: scale() is crucial for web developers and designers. While zoom offers a straightforward way to magnify elements, transform: scale() provides more control over the scaling behavior and its impact on the page layout.
Syntax
The zoom CSS property can be applied using various values to control the magnification level of an element. The syntax for the zoom property is straightforward and supports several types of values, including keywords, percentages, and numbers.
Here is the basic syntax for the zoom property:
/* Keyword values */zoom: normal;zoom: reset;
/* <percentage> values */zoom: 50%;zoom: 200%;
/* <number> values */zoom: 1.1;zoom: 0.7;
/* Global values */zoom: inherit;zoom: initial;zoom: revert;zoom: revert-layer;zoom: unset;Explanation of Syntax Components
- Keyword Values:
normal: Renders the element at its normal size.reset: Prevents the element from being magnified or reduced if the user applies non-pinch-based zooming (e.g., using keyboard shortcuts likeCtrl--orCtrl++). Note that usingresetis generally discouraged; the standardunsetvalue should be used instead.
- Percentage Values:
- Specifies the zoom factor as a percentage. A value of
100%is equivalent tonormal. Values larger than100%zoom in, while values smaller than100%zoom out.
- Specifies the zoom factor as a percentage. A value of
- Number Values:
- Specifies the zoom factor as a number. Equivalent to the corresponding percentage (e.g.,
1.0=100%=normal). Values larger than1.0zoom in, while values smaller than1.0zoom out.
- Specifies the zoom factor as a number. Equivalent to the corresponding percentage (e.g.,
- Global Values:
inherit: Inherits thezoomvalue from the parent element.initial: Sets thezoomvalue to its default (normal).revert: Resets thezoomvalue to the default specified by the user agent.revert-layer: Resets thezoomvalue to the default specified by the user agent, considering any cascade layers.unset: Resets thezoomvalue to its inherited value if it inherits, or toinitialif it does not.
By using the appropriate syntax and values, you can effectively control the magnification level of elements on your web page, enhancing the user experience and ensuring a responsive design.
Values
The zoom CSS property accepts various values that control the magnification level of an element. Understanding these values is essential for effectively using the zoom property in your web projects. Below is a detailed explanation of each value type:
normal
- Description: Renders the element at its normal size.
- Usage: This value is the default setting for the
zoomproperty, ensuring that the element is displayed at its original size without any magnification.
zoom: normal;reset
- Description: Prevents the element from being magnified or reduced if the user applies non-pinch-based zooming (e.g., using keyboard shortcuts like
Ctrl--orCtrl++). - Note: The use of
resetis generally discouraged. Instead, the standardunsetvalue should be used to achieve similar behavior.
zoom: reset;<percentage>
- Description: Specifies the zoom factor as a percentage.
- Usage: A value of
100%is equivalent tonormal. Values larger than100%zoom in, making the element appear larger, while values smaller than100%zoom out, making the element appear smaller.
zoom: 50%; /* Zooms out to 50% of the original size */zoom: 200%; /* Zooms in to 200% of the original size */<number>
- Description: Specifies the zoom factor as a number.
- Usage: Equivalent to the corresponding percentage (e.g.,
1.0is the same as100%, which is the same asnormal). Values larger than1.0zoom in, while values smaller than1.0zoom out.
zoom: 1.1; /* Zooms in to 110% of the original size */zoom: 0.7; /* Zooms out to 70% of the original size */Global Values
inherit: Inherits thezoomvalue from the parent element.initial: Sets thezoomvalue to its default (normal).revert: Resets thezoomvalue to the default specified by the user agent.revert-layer: Resets thezoomvalue to the default specified by the user agent, considering any cascade layers.unset: Resets thezoomvalue to its inherited value if it inherits, or toinitialif it does not.
zoom: inherit; /* Inherits the zoom value from the parent element */zoom: initial; /* Sets the zoom value to its default (normal) */zoom: revert; /* Resets the zoom value to the user agent default */zoom: revert-layer; /* Resets the zoom value to the user agent default, considering cascade layers */zoom: unset; /* Resets the zoom value to its inherited value or initial if it does not inherit */By using these values appropriately, you can effectively control the magnification level of elements on your web page, enhancing the user experience and ensuring a responsive design.
Formal Definition
The zoom CSS property is formally defined with specific attributes that dictate its behavior and usage. Understanding these attributes is crucial for effectively implementing the zoom property in your web projects. Here is a breakdown of its formal definition:
- Initial Value:
normal- The default value for the
zoomproperty isnormal, which means the element is rendered at its original size without any magnification.
- The default value for the
- Applies To: All elements
- The
zoomproperty can be applied to any HTML element, making it a versatile tool for controlling the magnification level across different parts of a web page.
- The
- Inherited: No
- The
zoomproperty is not inherited from the parent element. Each element must have its ownzoomvalue specified if magnification is desired.
- The
- Computed Value: As specified
- The computed value of the
zoomproperty is the same as the value specified in the CSS. This means that the browser will apply the exact magnification factor specified by the developer.
- The computed value of the
- Animation Type: Not animatable
- The
zoomproperty cannot be animated using CSS animations or transitions. This limitation is important to keep in mind when designing interactive elements that require smooth scaling effects.
- The
Formal Syntax
The formal syntax for the zoom property is as follows:
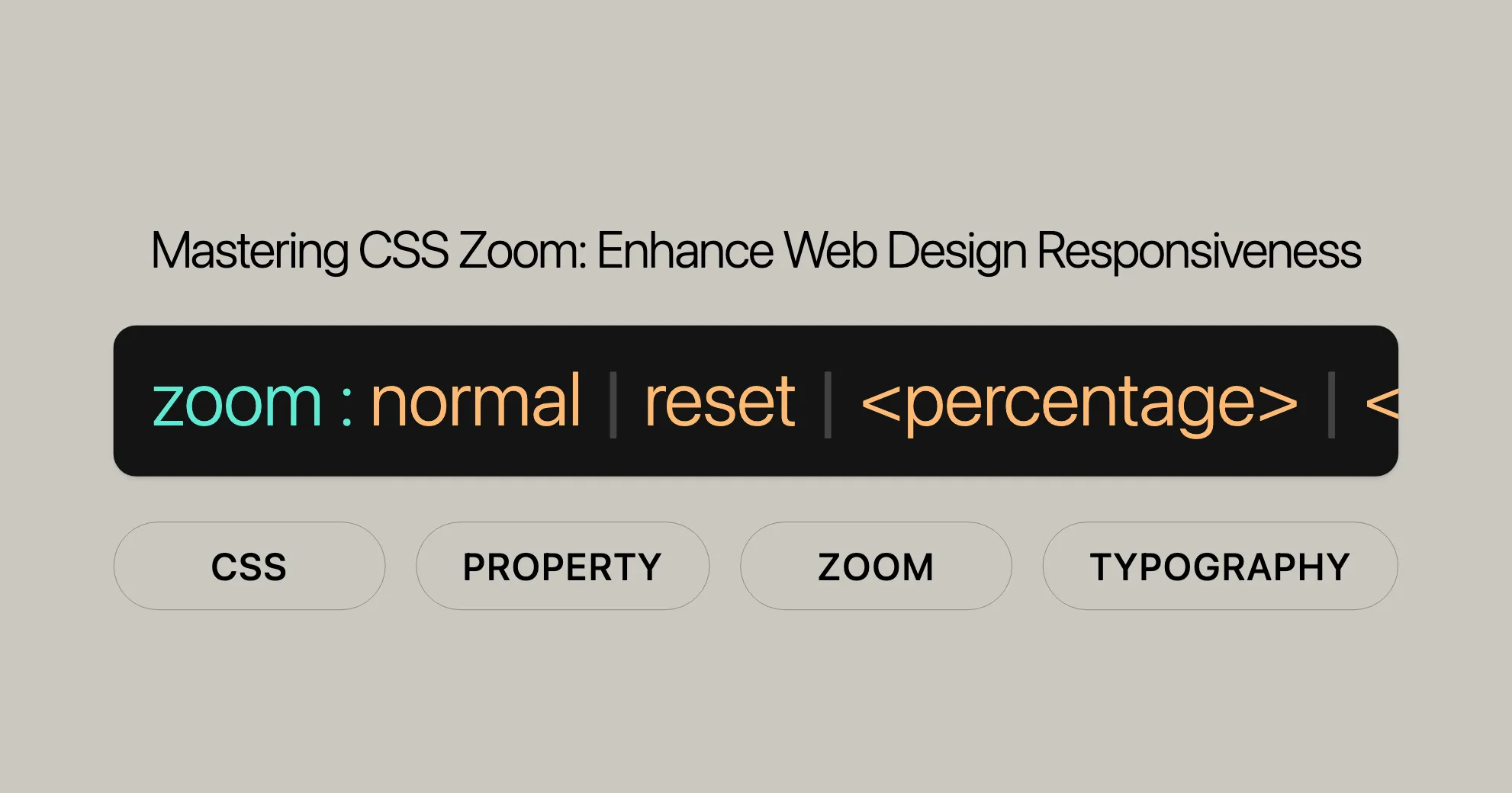
zoom = normal | reset | <number> | <percentage>Explanation of Formal Syntax Components
normal: Renders the element at its normal size.reset: Prevents the element from being magnified or reduced if the user applies non-pinch-based zooming (e.g., using keyboard shortcuts likeCtrl--orCtrl++). Note that usingresetis generally discouraged; the standardunsetvalue should be used instead.<number>: Specifies the zoom factor as a number. Equivalent to the corresponding percentage (e.g.,1.0is the same as100%, which is the same asnormal). Values larger than1.0zoom in, while values smaller than1.0zoom out.<percentage>: Specifies the zoom factor as a percentage. A value of100%is equivalent tonormal. Values larger than100%zoom in, while values smaller than100%zoom out.
By adhering to these formal definitions and syntax rules, you can ensure that the zoom property is used correctly and effectively in your web development projects. This will help you create responsive designs that enhance the user experience and adapt to different screen sizes and user preferences.
Examples
To better understand how the zoom property works in practice, let’s explore some examples that demonstrate its usage. These examples cover resizing paragraphs, resizing elements, and creating a zoom control.
Resizing Paragraphs
In this example, paragraph elements are zoomed using the zoom property. When a paragraph is hovered over, the zoom value is unset, returning the paragraph to its normal size.
HTML:
<p class="small">Small</p><p class="normal">Normal</p><p class="big">Big</p>CSS:
body { display: flex; align-items: center; justify-content: space-around; height: 100vh;}
.small { zoom: 75%;}.normal { zoom: normal;}.big { zoom: 2.5;}p:hover { zoom: unset;}Resizing Elements
In this example, div elements are zoomed using the normal, <percentage>, and <number> values.
HTML:
<div id="a" class="circle"></div><div id="b" class="circle"></div><div id="c" class="circle"></div>CSS:
div.circle { width: 25px; height: 25px; border-radius: 100%; vertical-align: middle; display: inline-block;}div#a { background-color: gold; zoom: normal; /* circle is 25px diameter */}div#b { background-color: green; zoom: 200%; /* circle is 50px diameter */}div#c { background-color: blue; zoom: 2.9; /* circle is 72.5px diameter */}Creating a Zoom Control
In this example, a select field is used to change the zoom level of an element.
HTML:
<section class="controls"> <label for="zoom"> Zoom level <select name="zoom" id="zoom"> <option value="0.5">Extra Small</option> <option value="0.75">Small</option> <option value="normal" selected>Normal</option> <option value="1.5">Large</option> <option value="2">Extra Large</option> </select> </label></section>
<p class="zoom-notice">CSS zoom is not supported</p>
<section class="content"> <h1>This is the heading</h1> <p> Lorem ipsum dolor, sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Placeat inventore ea eveniet, fugiat in consequatur molestiae nostrum repellendus nam provident repellat officiis facilis alias facere obcaecati quos sunt voluptas! Iste. </p> <p> Lorem ipsum dolor, sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Placeat inventore ea eveniet, fugiat in consequatur molestiae nostrum repellendus nam provident repellat officiis facilis alias facere obcaecati quos sunt voluptas! Iste. </p></section>CSS:
html { --zoom-level: normal;}.content { max-width: 60ch; margin: auto; zoom: var(--zoom-level);}
.controls,.zoom-notice { display: flex; justify-content: space-around;}.zoom-notice { color: red;}
@supports (zoom: 1) { .zoom-notice { display: none; }}JavaScript:
const zoomControl = document.querySelector("#zoom");const content = document.querySelector(".content");const updateZoom = () => { content.style = `--zoom-level: ${zoomControl.value}`;};zoomControl.addEventListener("change", updateZoom);Browser Compatibility
The zoom CSS property is a relatively new feature, and its compatibility varies across different browsers and devices. Here’s a quick overview:
-
Latest Devices and Browser Versions:
- The
zoomproperty works across the latest devices and browser versions. However, it might not be supported on older devices or browsers.
- The
-
Key Browsers:
- Google Chrome: Supports the
zoomproperty in its latest versions. - Mozilla Firefox: The
zoomproperty is supported in the latest versions. - Microsoft Edge: Supports the
zoomproperty in its latest versions. - Safari: The
zoomproperty is supported in the latest versions. - Opera: Supports the
zoomproperty in its latest versions.
- Google Chrome: Supports the
-
Legacy Browsers:
- Internet Explorer: The
zoomproperty has limited support.
- Internet Explorer: The
To ensure compatibility, perform thorough testing on multiple browsers and devices. You can use the @supports CSS feature to check if the browser supports the zoom property:
@supports (zoom: 1) { .zoom-notice { display: none; }}Further Resources
For further learning, check out these resources:
- MDN Web Docs: CSS
zoom - CSS-Tricks: Zoom Property
- W3C CSS Viewport Module
- Can I Use: CSS Zoom
- CSS Transform: scale()
- CSS Overflow
By exploring these resources, you can gain a deeper understanding of the zoom property and its applications in web development and design. These references will help you create more dynamic, responsive, and user-friendly web pages.
 สร้างเว็บไซต์ 1 เว็บ ต้องใช้งบเท่าไหร่? เจาะลึกทุกองค์ประกอบ website development cost อยากสร้างเว็บไซต์แต่ไม่มั่นใจในเรื่องของงบประมาณ อ่านสรุปเจาะลึกตั้งแต่ดีไซน์, ฟังก์ชัน และการดูแล พร้อมตัวอย่างงบจริงจาก Till it’s done ที่แผนชัด งบไม่บานปลายแน่นอน
สร้างเว็บไซต์ 1 เว็บ ต้องใช้งบเท่าไหร่? เจาะลึกทุกองค์ประกอบ website development cost อยากสร้างเว็บไซต์แต่ไม่มั่นใจในเรื่องของงบประมาณ อ่านสรุปเจาะลึกตั้งแต่ดีไซน์, ฟังก์ชัน และการดูแล พร้อมตัวอย่างงบจริงจาก Till it’s done ที่แผนชัด งบไม่บานปลายแน่นอน  Next.js สอน 14 ขั้นตอนเบื้องต้น: สร้างโปรเจกต์แรกใน 30 นาที เริ่มต้นกับ Next.js ใน 14 ขั้นตอนเพียงแค่ 30 นาที พร้อม SSR/SSG และ API Routes ด้วยตัวอย่างโค้ดง่าย ๆ อ่านต่อเพื่อสร้างโปรเจ็กต์แรกได้ทันทีที่นี่
Next.js สอน 14 ขั้นตอนเบื้องต้น: สร้างโปรเจกต์แรกใน 30 นาที เริ่มต้นกับ Next.js ใน 14 ขั้นตอนเพียงแค่ 30 นาที พร้อม SSR/SSG และ API Routes ด้วยตัวอย่างโค้ดง่าย ๆ อ่านต่อเพื่อสร้างโปรเจ็กต์แรกได้ทันทีที่นี่  วิธีสมัคร Apple Developer Account เพื่อนำแอปขึ้น App Store ทีละขั้นตอน อยากปล่อยแอปบน App Store ระดับโลก มาอ่านคู่มือสมัคร Apple Developer Account พร้อมเคล็ดลับ TestFlight และวิธีอัปโหลดที่ง่ายในบทความเดียวนี้ได้เลย
วิธีสมัคร Apple Developer Account เพื่อนำแอปขึ้น App Store ทีละขั้นตอน อยากปล่อยแอปบน App Store ระดับโลก มาอ่านคู่มือสมัคร Apple Developer Account พร้อมเคล็ดลับ TestFlight และวิธีอัปโหลดที่ง่ายในบทความเดียวนี้ได้เลย  TypeScript Interface คืออะไร? อธิบายพร้อมวิธีใช้และข้อแตกต่างจาก Type เรียนรู้วิธีใช้ TypeScript Interface เพื่อสร้างโครงสร้างข้อมูลที่ปลอดภัยและเข้าใจง่าย พร้อมเปรียบเทียบข้อดีข้อแตกต่างกับ Type ที่คุณต้องรู้ ถูกรวมเอาไว้ในบทความนี้แล้ว
TypeScript Interface คืออะไร? อธิบายพร้อมวิธีใช้และข้อแตกต่างจาก Type เรียนรู้วิธีใช้ TypeScript Interface เพื่อสร้างโครงสร้างข้อมูลที่ปลอดภัยและเข้าใจง่าย พร้อมเปรียบเทียบข้อดีข้อแตกต่างกับ Type ที่คุณต้องรู้ ถูกรวมเอาไว้ในบทความนี้แล้ว  Material-UI (MUI) คืออะไร อยากสร้าง UI สวยงามและเป็นมืออาชีพในเวลาอันรวดเร็วใช่ไหม มาทำความรู้จักกับ Material-UI (MUI) ที่ช่วยให้คุณพัฒนาแอปพลิเคชันบน React ได้ง่ายและดูดีในทุกอุปกรณ์
Material-UI (MUI) คืออะไร อยากสร้าง UI สวยงามและเป็นมืออาชีพในเวลาอันรวดเร็วใช่ไหม มาทำความรู้จักกับ Material-UI (MUI) ที่ช่วยให้คุณพัฒนาแอปพลิเคชันบน React ได้ง่ายและดูดีในทุกอุปกรณ์  เปรียบเทียบ 3 วิธีติดตั้ง install node js บน Ubuntu: NVM vs NodeSource vs Official Repo แบบไหนดีที่สุด? เรียนรู้วิธีติดตั้ง Node.js บน Ubuntu ด้วย NVM, NodeSource หรือ Official Repo เลือกวิธีที่เหมาะกับความต้องการของคุณ พร้อมเปรียบเทียบ เพื่อการพัฒนาที่มีประสิทธิภาพ!
เปรียบเทียบ 3 วิธีติดตั้ง install node js บน Ubuntu: NVM vs NodeSource vs Official Repo แบบไหนดีที่สุด? เรียนรู้วิธีติดตั้ง Node.js บน Ubuntu ด้วย NVM, NodeSource หรือ Official Repo เลือกวิธีที่เหมาะกับความต้องการของคุณ พร้อมเปรียบเทียบ เพื่อการพัฒนาที่มีประสิทธิภาพ! พูดคุยกับซีอีโอ
We'll be right here with you every step of the way.
We'll be here, prepared to commence this promising collaboration.
Whether you're curious about features, warranties, or shopping policies, we provide comprehensive answers to assist you.


